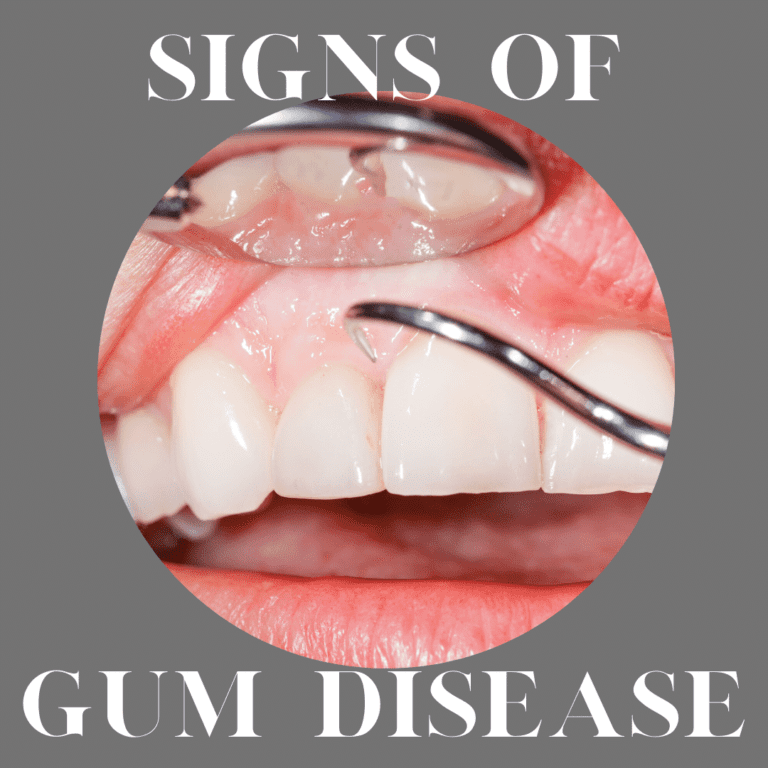
Practicing good daily oral hygiene and attending regular dental appointments is important to maintain your oral health. While many people think that brushing and flossing only benefit their teeth, these behaviors are actually important for the health of their gums as well. This is because the same bacteria responsible for tooth decay can also accumulate along the gum line and result in gum disease.
In its mild form, gum disease is known as gingivitis, while advanced gum disease is known as periodontitis. Unfortunately, having some form of gum disease is more common than many people think and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has found that 47.2% of adults over the age of 30 and 70.1% of adults over the age of 65 have some form of gum disease.
Part of the reason why gum disease is so common is because many people don’t know the symptoms of gum disease and don’t even realize they have it until it has progressed to the advanced stages. At this point, however, advanced gum disease can only be managed with treatment and cannot be reversed. Therefore, it is important to recognize some of the most common signs of gum disease before it progresses.
Visual Abnormalities
When you look at your gums, they should be a coral pink color or slightly darker if you have darker skin. However, your gums should not be a deep pink or red color and if they are, it could indicate that they are inflamed and possibly affected by gum disease. Additionally, your gums should be free of swelling and they should not bleed while you brush and floss. Gums that appear to be swollen or that bleed easily are other signs that your gums are inflamed and possibly affected by gum disease.
Receding Gums
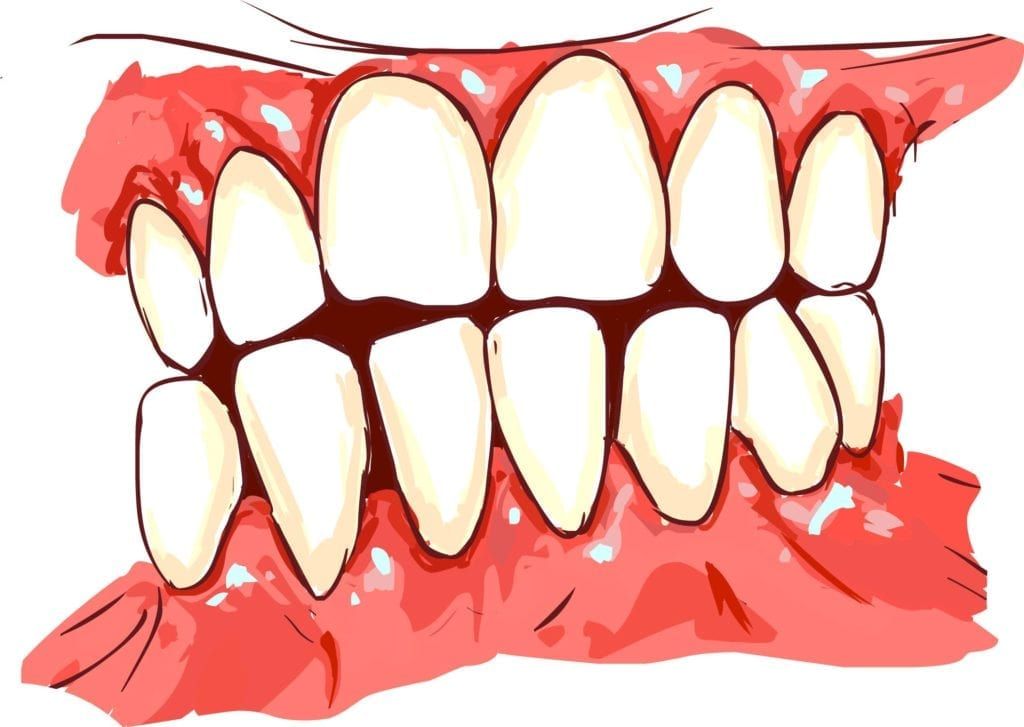
Gum recession is the term used to describe gums that have begun to pull away from the tooth and gradually expose the tooth roots. It can occur for a number of reasons, however in cases where gum disease is to blame, gum recession occurs as a reaction to the excess bacteria along the gum line. Unfortunately, it is a vicious cycle because gum recession causes the formation of gum pockets, which house bacteria, which causes more gum recession. In cases of severe gum recession, the teeth look abnormally large and they can even become loose, shift in position, or fall out.
Pain
The most common type of pain associated with gum disease is known as tooth sensitivity, which is a sudden deep ache that occurs when consuming foods or beverages that are hot, cold, or excessively sweet. Tooth sensitivity associated with gum disease happens when gum recession has exposed the tooth roots. Although gum pain or tenderness can be associated with gum disease, it is rare and only occurs when the gums are severely inflamed. In fact, most people with gum disease never experience any pain.
As you can see, there are a few key signs that can signal the presence of gum disease, including: visual abnormalities, gum recession, and pain. Oftentimes, changes in visual appearance are the first sign of gum disease, followed by gum recession and then pain. However each case of gum disease can present itself differently, so any of these symptoms should be immediately evaluated by your dentist to confirm a diagnosis of gum disease and receive the necessary treatment.